Case studies of successful EST3 to EST4 upgrades
In recent years, many organizations have undertaken the task of upgrading their EST life safety systems from EST3 to the next generation EST4. This article presents a comprehensive analysis of successful case studies in this area, highlighting the key factors that contributed to their achievements. Understanding the need for such upgrades, the technical aspects involved, evaluating the success, and learning lessons from these experiences are vital for organizations seeking to embark on similar journeys.
Understanding the Need for Upgrading from EST3 to EST4
As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, it is crucial for organizations to stay up-to-date with the latest systems and equipment. Upgrading from EST3 to EST4 offers a range of benefits that make it a worthwhile investment. With the announced end of service period approaching, organizations can make informed decisions regarding the upgrade process and ensure the safety and efficiency of their operations.
The Evolution from EST3 to EST4
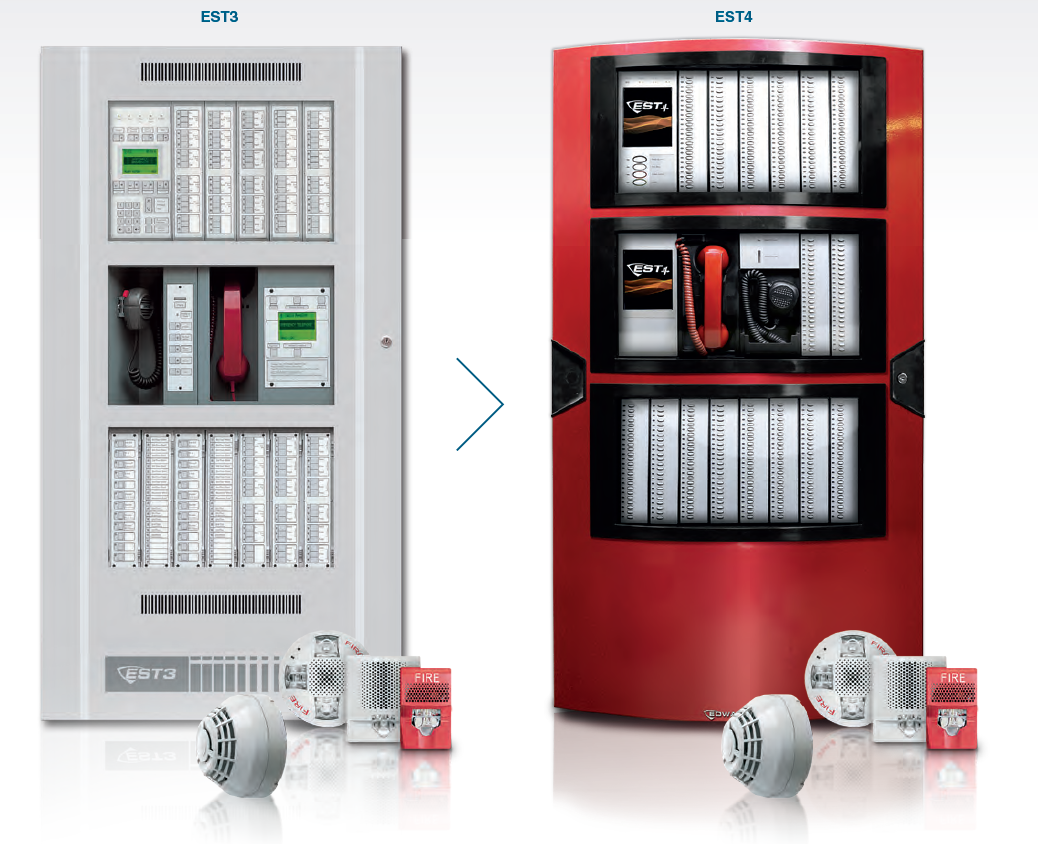
The EST4 life safety system represents a significant evolution from its predecessor, EST3. With the ever-growing demands of modern requirements, the EST4 system incorporates cutting-edge technologies and features that enhance safety, efficiency, and reliability. Understanding the key differences between these two systems will help organizations appreciate the value of upgrading to EST4.
The EST4 represents an investment-forward platform designed for the future. The uniquely designed hardware allows backwards compatibility for EST3 retrofits while at the same time introducing a future ready flexible feature set.
EST4 is a modular system, which enables users to customize the platform for their particular application. This optimizes system cost while allowing users flexibility to support future expansion.
The EST4 also introduces a number of network related enhancements. These enhancements allow for maximum flexibility and support for a wide range of network configurations. In addition, networking hardware utilizes a UL-listed proxy firewall, which helps protect systems from cybersecurity threats.
The system also includes improvements to support Emergency Voice Communications. Distributed audio and support for up to 100 channels of audio allow for messages to be tailored to specific applications and delivered where and when they are needed most.
Key Benefits of Upgrading
One of the primary reasons organizations choose to upgrade to EST4 is the host of benefits it brings. EST4 was designed with upgrading in mind and protects building owners investment in their life safety system. Wiring, peripheral devices, and many fire alarm control panel components can be reused as part of the upgraded system.
The EST4 system brings a number of benefits to building owners in the areas of communications, cybersecurity, and user interface. The onboard webserver allows for remote device independent access to system status and reports. Built-in E-mail and E-mail-to-SMS messaging enable instant notification of specific event types to be sent to appropriate personnel. A large full-color LCD touchscreen with tactile buttons provides fast, intuitive access to service and first responder functions. Five-color LED Indicators allow users and first responders to quickly determine system status at a glance.
Enhancements to the communications protocol allow for backwards compatibility and less expensive upgrades. Network data, audio data, and telephone data share a single twisted pair or single fiber strand, requiring up to 75 percent less cabling which means a substantial cost savings in material and labor. Existing systems supporting only network data can also support voice audio, so upgrades can add value and extend system life safety capabilities in retrofit situations.
In conclusion, upgrading from EST3 to EST4 is a strategic decision that organizations must consider to stay ahead in the ever-evolving landscape of life safety technology and to maintain compliance with ever changing life safety codes. The advanced communications enhancements, backwards compatibility, and greater flexibility in system configuration offered by EST4 make it a compelling choice for organizations seeking to enhance safety, efficiency, and reliability. By understanding the need for this transition, organizations can make informed decisions and ensure the seamless upgrades to EST4.
The Technical Aspects of EST3 to EST4 Upgrades
While understanding the need for upgrading is essential, it is equally important to have a firm grasp of the technical aspects involved in the transition from EST3 to EST4. This section delves into the details of the upgrade process, potential challenges, and the solutions that can be implemented to overcome them.
The Upgrade Process Explained
The upgrade process from EST3 to EST4 is a complex undertaking that requires meticulous planning and execution. It involves several stages that organizations need to follow to ensure a successful transition.
The first stage is system assessment. This involves evaluating the current EST3 system to identify any hardware or software limitations that may impact the upgrade process. It is crucial to conduct a thorough assessment to determine the scope of the upgrade and the necessary resources required.
Once the system assessment is complete, the next stage is hardware and software upgrades. This involves replacing outdated hardware components and updating the software to the latest version compatible with EST4. It is essential to ensure compatibility between the new hardware and software to avoid any compatibility issues during the upgrade.
After the hardware and software upgrades are completed, the system testing phase begins. This phase involves rigorous testing of the upgraded system to ensure its functionality, reliability, and compatibility with existing equipment. It is crucial to conduct comprehensive testing to identify and resolve any issues before the upgraded system is fully implemented.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
While the benefits of upgrading to EST4 are evident, organizations may encounter challenges during the transition. It is important to be aware of these challenges and have solutions in place to mitigate their impact.
One potential challenge is compatibility issues with existing equipment. Upgrading to EST4 may require additional hardware components or software updates that may not be compatible with the current equipment. To overcome this challenge, organizations can conduct thorough compatibility testing before the upgrade and identify any necessary hardware or software changes required to ensure compatibility.
Another challenge organizations may face is potential disruptions to operations during the upgrade process. Upgrading a critical system like EST3 to EST4 may require temporary shutdowns or limited functionality, which can impact daily operations. To minimize disruptions, organizations can develop a detailed implementation plan that includes scheduled downtime, alternative communication methods, and contingency measures to ensure business continuity.
Employee training is another challenge that organizations may encounter during the transition. Upgrading to EST4 may introduce new features, functionalities, and interface changes that require employees to acquire new skills and knowledge. To address this challenge, organizations can provide comprehensive training programs to educate employees on the upgraded system, its benefits, and how to effectively utilize its features.
In conclusion, the technical aspects of upgrading from EST3 to EST4 are complex but manageable with proper planning and execution. By following a systematic upgrade process and proactively addressing potential challenges, organizations can successfully transition to EST4 and enjoy its enhanced capabilities and benefits.
Evaluating the Success of EST3 to EST4 Upgrades
Once the upgrade process is complete, it is essential for organizations to assess the success of the endeavor. Evaluating the impact of the transition will not only enable organizations to gauge the effectiveness of the upgrade but also identify areas for improvement.
When organizations embark on the journey of upgrading their EST3 system to EST4, they are making a significant investment in their life safety infrastructure. It is crucial for them to ensure that this investment pays off and delivers the desired outcomes. This is where evaluating the success of the upgrade becomes paramount.
One of the primary ways organizations can measure the success of the EST3 to EST4 upgrade is by establishing measurable metrics. These metrics serve as benchmarks against which the performance of the upgraded system can be evaluated. By defining and analyzing these metrics, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of the upgrade’s overall performance.
Metrics for Measuring Upgrade Success
Organizations should establish measurable metrics to evaluate the success of the EST3 to EST4 upgrade. These metrics may include reduced system downtime, improved response time, increased system reliability, enhanced security measures, and streamlined processes. By tracking these metrics, organizations can quantitatively assess the impact of the upgrade and identify areas where further enhancements may be required.
Reduced system downtime is a critical metric that organizations should consider when evaluating the success of the upgrade. By minimizing the time during which the system is unavailable, organizations can ensure uninterrupted operations and maximize productivity. Improved response time is another important metric as it directly affects the efficiency of day-to-day operations. Organizations should aim for faster response times, enabling users to access and utilize the upgraded system with minimal delays.
In addition to reduced downtime and improved response time, increased system reliability is a key metric for measuring the success of the EST3 to EST4 upgrade. Organizations should assess whether the upgraded system experiences fewer errors, glitches, or failures compared to its predecessor. Enhanced system reliability not only boosts user confidence but also minimizes the need for troubleshooting and maintenance, resulting in cost savings for the organization.
Long-Term Impacts of the Upgrade
Successful upgrade projects have long-term implications for organizations. This section explores the lasting impacts of transitioning from EST3 to EST4, such as increased system lifespan, improved maintenance strategies, and better integration with other systems. Understanding these long-term benefits will help organizations realize the full value of their investment.
One of the significant long-term impacts of the EST3 to EST4 upgrade is an increased system lifespan. By migrating to a newer and more advanced system, organizations can extend the useful life of their building life safety infrastructure. This not only reduces the frequency of future upgrades but also provides a stable platform for future enhancements and expansions.
Improved maintenance strategies are another long-term benefit of the upgrade. With EST4, organizations can leverage advanced diagnostic tools and automated maintenance processes, making it easier to identify and address issues proactively. This proactive approach to maintenance minimizes system downtime and reduces the risk of critical failures, ensuring smooth operations and uninterrupted service delivery.
Furthermore, the EST3 to EST4 upgrade enables better integration with other systems. In today’s interconnected world, seamless integration with various software applications and hardware devices is crucial for organizations. EST4 offers enhanced compatibility and interoperability, allowing organizations to integrate their fire alarm systems with other security systems, building management systems, and emergency response systems. This integration enhances overall situational awareness and enables a more coordinated and efficient response in emergency situations.
In conclusion, evaluating the success of the EST3 to EST4 upgrade is essential for organizations to assess the effectiveness of the transition and identify areas for improvement. By establishing measurable metrics and considering the long-term impacts of the upgrade, organizations can gain valuable insights and make informed decisions to maximize the value of their investment.
Lessons Learned from Successful EST3 to EST4 Upgrades
While case studies of successful upgrades provide valuable insights, it is equally important to distill the lessons learned from these experiences. This section offers guidance by highlighting key best practices and common pitfalls to avoid during the upgrade process.
Upgrading from EST3 to EST4 is a significant undertaking for organizations. It involves migrating to a new and improved system that offers enhanced features and capabilities. However, to ensure a smooth and successful transition, organizations need to follow a set of best practices and be aware of potential pitfalls.
Best Practices for a Smooth Upgrade
Based on the successful case studies examined, this section presents a set of best practices that organizations can follow to ensure a seamless transition. Thorough planning is essential before embarking on the upgrade journey. This includes conducting a thorough assessment of the existing EST3 system, identifying the specific goals and objectives of the upgrade, and developing a detailed roadmap for the implementation.
Effective communication with all stakeholders is another crucial aspect of a smooth upgrade. Organizations should involve key personnel from different departments, such as IT, operations, and maintenance, to ensure that everyone is aligned and informed about the upgrade process. Regular communication channels, such as meetings, emails, and progress reports, should be established to keep all stakeholders updated on the project’s status.
Comprehensive training programs for employees are vital to the success of the upgrade. Organizations should invest in training sessions that cover the new features and functionalities of the EST4 system. This will help employees adapt to the changes and make the most of the upgraded system. Training should be conducted in a phased approach, starting with key personnel and gradually extending to all users.
By adopting these practices, organizations can minimize disruptions and maximize the benefits of the upgrade. A well-planned and well-executed upgrade can lead to improved safety, efficiency, and reliability in the organization’s operations.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls in the Upgrade Process
Even with careful planning and implementation, organizations may come across common pitfalls during the EST3 to EST4 upgrade. This section highlights these potential pitfalls and provides guidance on how to avoid them.
Insufficient system testing is a common pitfall that organizations should be aware of. It is crucial to thoroughly test the EST4 system before going live to ensure that it functions correctly and meets the organization’s requirements. Testing should include scenarios that simulate real-life situations to identify any potential issues or bugs.
Inadequate user training is another pitfall that organizations should avoid. Employees need to be adequately trained on the new system to ensure a smooth transition. Training should not be limited to just the technical aspects of the EST4 system but should also cover any changes in workflows or processes. This will help employees adapt to the new system more effectively.
Lack of post-upgrade support is another common pitfall that organizations should address. After the upgrade, organizations should provide ongoing support to users to address any questions or issues that may arise. This can be done through a dedicated support team or by providing resources such as user manuals and online forums.
By being aware of these challenges and taking proactive measures to mitigate risks, organizations can ensure a successful upgrade. Learning from the experiences of others and avoiding common pitfalls will contribute to a smoother transition to the EST4 system.
By examining the case studies of successful EST3 to EST4 upgrades, it becomes evident that organizations can achieve significant benefits through this transition. Understanding the need for upgrading, the technical aspects involved, evaluating the success, and learning lessons from these successful case studies will equip organizations with the knowledge necessary to embark on their own successful EST3 to EST4 upgrade journey. Through careful planning, execution, and continuous improvement, organizations can leverage the capabilities of EST4 to enhance safety, efficiency, and reliability in their operations.